How to Choose SVM Threshold
The classification model for predicting pseudouridine sites was based on support vector machine(SVM). The software LIBSVM3.20(Chang and Lin, 2001 Software available at http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/_cjlin/libsvm) was employed in this work, in which a radial basis function(RBF) was chosen as the kernel function.
For a given test example x, an SVM classifier outputs a predictive value that represents the distance of x from the optimal separating hyperplane in the feature space. we used a technique known as binning to convert predictive values to posterior probabilities (Kwok, 1999), which was implemented internally in the LIB-SVM software package. The larger the posterior probability is for a site, the more likely the site is a pseudouridine site. The threshold, allowed user to choose in web page, is to filter this posterior probability. Therefore, if user want to have more predictions, then choose a lower probability; while if user want to have only the most reliable predictions, then choose a higher probability.
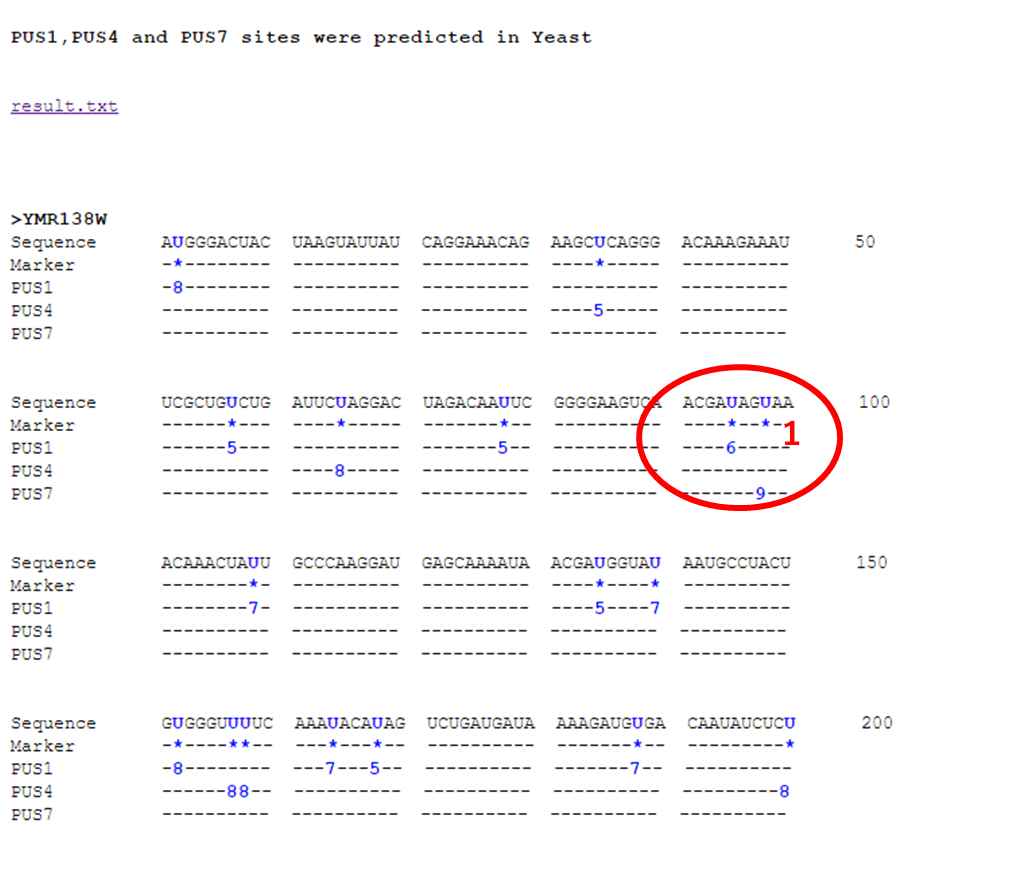
More, to make it easy to display in web page, we convert this probability to M-score by equation: M-score=floor(10*probability). The M-score ("6" and "9" in red circle "1" in Figure 1) is to show whether a prediction is reliable or not. M-score can be 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 or 10. The higher the M-score, the more reliable the prediction.
Reference
[1]Chang, C.-C., Lin, C.-J., , LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines Software available at http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libsvm, 2001.
[2]Kwok, J.Y. (1999) Moderating the outputs of support vector machine classifiers, IEEE transactions on neural networks / a publication of the IEEE Neural Networks Council, 10, 1018-1031.